
May 24, 2015 Avogadro's law investigates the relationship between the amount of gas (n) and volume (v). It's a direct relationship, meaning the volume of a gas is directly propotional to the number of moles the gas sample present. The constants in this relationship would be the temperature (t) and pressure (p) The equation for this law is: n1/v1 = n2/v2. Avogadro’s Law (sometimes referred to as Avogadro’s hypothesis or Avogadro’s principle) is a gas law; it states that under the same pressure and temperature conditions, equal volumes of all gases contain the same number of molecules.

What Is Avogadro's Law In Chemistry

Avogadro Law Chemistry Class 11


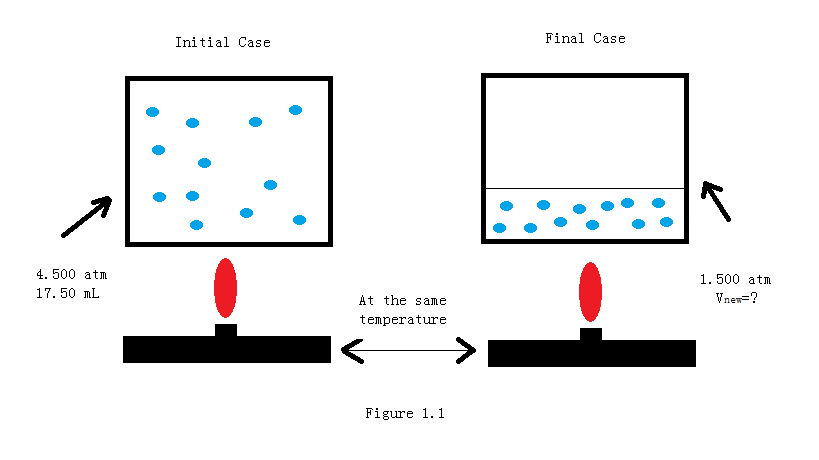
Which Statement Best Describes Avogadro's Law
Unit 5 - Gases > Avogadro's LawPOWERPOINT
Avogadro's Law - 'equal volumes of gases at the same (constant) temperature and pressure contain the same number of molecules regardless of their chemical nature and physical properties'
- So, let's explain this law (also seen in the figure below):
- There are 3 balloons where 1 balloon contains 1 mole of Argon, another has 1 mole of Oxygen, and the 3rd balloon containing Nitrogen
- The pressure and temperature are 1 atm and 0oC, respectively.
- All three balloons occupy a volume of 22.4 L
- Therefore, avogadro's law states that 1 mole of ANY gas is 22.4L at STP. (1 mole = 22.4 L)
- EXAMPLE #1: At STP, what volume will 2.5 moles of nitrogen occupy?
- Avogadro also stated that if you change the number of molecules, the volume will also be affected.
Avogadro's Law equation Convert mp4 to mkv file.
- Example #1 - A 5.00 mole sample of gas occupies 2.00 L at room temperature and normal atmospheric pressure. If the pressure and temperature remain constant, what would happen to the volume if the number of moles were increased to 10.0 moles?
- Example #2 - A sample of Nitrogen gas has 1.70 moles and occupies 3.80 L at room temperature and normal atmospheric pressure. How many moles of nitrogen gas must there be in order for a sample to occupy 1.45 L?
Avogadro's Law |
|






